Text erkannt:
Arbeitsblatt-Integralrechnung, Stammfunktion
1) In welchen Fällen ist \( \mathrm{F} \) eine Stammfunktion der Funktion \( \mathrm{f} \) ?
A) \( \square f(x)=0, F(x)=x \)
D) \( \square f(x)=3 \cdot \sqrt{x}, F(x)=2 x \cdot \sqrt{x} \)
B) \( \square f(x)=\ln x, F(x)=\frac{1}{x} \)
E) \( \square f(x)=e^{2 x}, \quad F(x)=2 e^{2 x} \)
c) \( \square f(x)=\frac{5}{x^{2}}+1, F(x)=\frac{5}{x}+x \)
F) \( \square f(x)=4 x^{7}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}, F(x)=\frac{x^{3}}{2}+2 \cdot \sqrt{x} \)
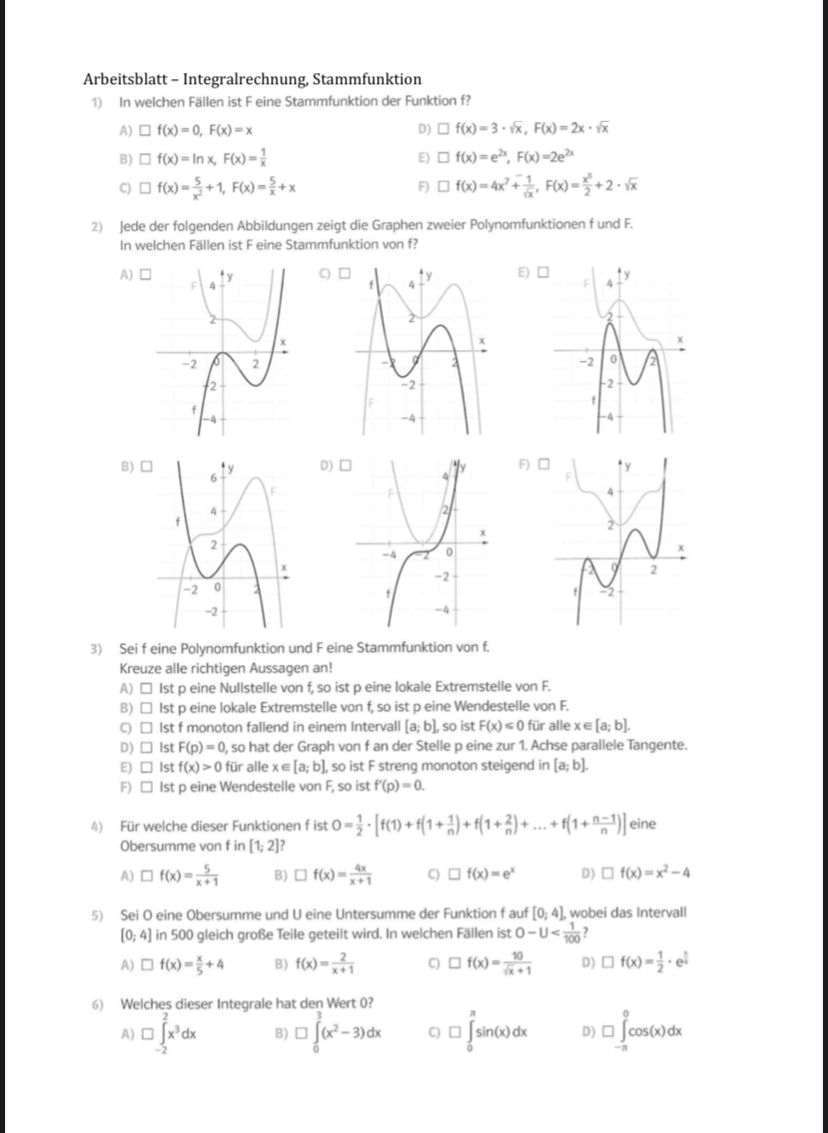
2) Jede der folgenden Abbildungen zeigt die Graphen zweier Polynomfunktionen \( \mathrm{f} \) und \( \mathrm{F} \).
In welchen Fällen ist F eine Stammfunktion von \( \mathrm{f} \) ?
A) \( \square \)
B) \( \square \)
D)
F) \( \square \)
3) Sei f eine Polynomfunktion und \( \mathrm{F} \) eine Stammfunktion von \( \mathrm{f} \).
Kreuze alle richtigen Aussagen an!
A) \( \square \) Ist p eine Nullstelle von \( \mathrm{f} \), so ist p eine lokale Extremstelle von \( \mathrm{F} \).
B) \( \square \) Ist p eine lokale Extremstelle von \( \mathrm{f} \), so ist p eine Wendestelle von \( \mathrm{F} \).
C) \( \square \) ist \( f \) monoton fallend in einem Intervall \( [a ; b] \), so ist \( F(x)<0 \) für alle \( x \in[a ; b] \)
D) \( \square \) Ist \( F(p)=0 \), so hat der Graph von \( f \) an der Stelle p eine zur 1 . Achse parallele Tangente.
E) \( \square \) ist \( f(x)>0 \) für alle \( x \in[a ; b] \) so ist \( F \) streng monoton steigend in \( [a ; b] \).
F) \( \square \) Ist p eine Wendestelle von \( \mathrm{F} \), so ist \( \mathrm{f}(\mathrm{p})=0 \).
4) Für welche dieser Funktionen \( f \) ist \( 0=\frac{1}{2} \cdot\left[f(1)+f\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)+f\left(1+\frac{2}{n}\right)+\ldots+f\left(1+\frac{n-1}{n}\right)\right] \) eine
Obersumme von \( f \) in \( [1 ; 2] ? \)
\( \begin{array}{ll}\text { A) } \square f(x)=\frac{5}{x+1} & \text { B) } \square f(x)=\frac{4 x}{x+1}\end{array} \)
c) \( \square f(x)=e^{x} \)
D) \( \square f(x)=x^{2}-4 \)
5) Sei O eine Obersumme und U eine Untersumme der Funktion \( f \) auf \( [0 ; 4] \), wobei das intervall \( [0 ; 4] \) in 500 gleich große Teile geteilt wird. In welchen Fällen ist \( \mathrm{O}-\mathrm{U}<\frac{1}{100} ? \)
A) \( \square f(x)=\frac{x}{5}+4 \)
B) \( f(x)=\frac{2}{x+1} \quad \) c) \( \square f(x)=\frac{10}{\sqrt{x}+1} \)
D) \( \square f(x)=\frac{1}{2} \cdot \mathrm{e}^{2} \)
6) Welches dieser Integrale hat den Wert 0? \( \int x^{3} d x \)
4) \( \square \int\left(x^{2}-3\right) d \)
c) \( \square \int \sin (x) d x \)
D) \( \square \int \cos (x) d x \)