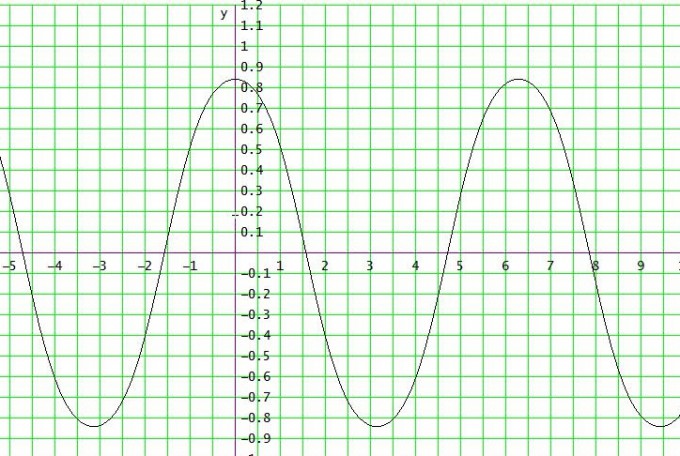
f(x) = sin(cos(x)) D = ℝ
Nullstellen:
sin(cos(x) = 0
Sinus hat die Nullstellen k • π mit k∈ℤ
⇔ cos(x) = k • π mit k∈ℤ
⇔ cos(x) = 0 [ weil -1 ≤ cos(x) ≤ 1 ]
⇔ x = π/2 + k • π mit k∈ℤ
Extremwerte:
f'(x) = -sin(x) • cos(cos(x))
⇔ sin(x) = 0 oder cos(cos(x)) = 0
⇔ x = k•π oder cos(x) = π/2 + k • π
Letzteres hat keine Lösung wegen -1 ≤ cos(x) ≤ 1
⇔ x = k • π k∈ℤ
Also: H ( 2k • π | sin(1) ) ≈ ( 2k • π | 0,841 ) , T ( (2k+1) • π | - sin(1) )
Monotonieintervalle (k∈ℤ) :
[ k•π ; (k+1)•π ] streng monoton fallend
[ (k-1)•π ; k•π ] streng monoton steigend
Gruß Wolfgang