Hallo Nadin :-),
f(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d [ Normalform ]
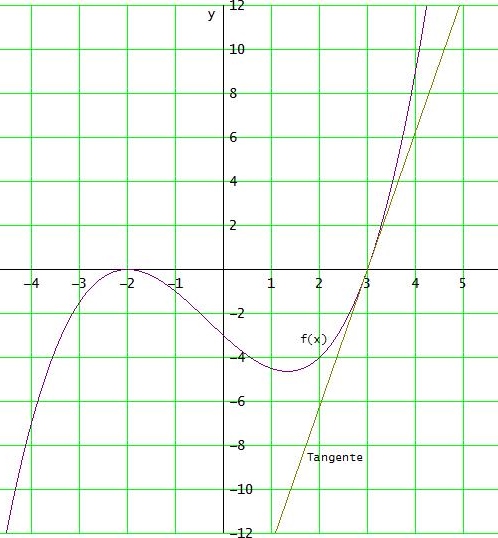
f(x) = a • (x + 2)2 • (x - n) [ Nullstellenform ]
( Nullstellenform, x = -2 ist doppelte Nullstelle [ berührt x-Achse ], Nullstelle n noch nicht bekannt )
f ''(-2) = -2,5 ( Krümmung f ''(x) = -2,5 an der stelle x = -2 )
f '(3) = 6,25 ( Steigung f '(x) = 6,25 an der stelle x = 3 )
f '(x) und f ''(x) ausrechnen und das Gleichungssystem mit zwei Unbekannten lösen:
f '(x) = a·(x + 2)·(3·x - 2·n + 2)
f ''(x) = 2·a·(3·x - n + 4)
f '(3) = 5·a·(11 - 2·n) = 6.25 G1
f ''(-2) = - 2·a·(n + 2) = -2.5 G2
G1/G2: -2,5 • ( 11 - 2n) / (n+2) = -2,5 → 11 - 2n = n + 2 → n = 3
n in G2 → -10a = -2,5 → a = 1/4
a,b einsetzen in f(x) = a • (x + 2)2 • ( x - n) [vgl. Antwort]
f(x) = 1/4 • (x+2)2 • (x-3) [ Nullstellenform ]
ausmultiplizieren:
f(x) = 1/4 • x3 + 1/4 • x2 - 2 • x - 3 [ Normalform ]
Gruß Wolfgang