Hallo Klara,
In der Aufgabenstellung steht, dass das Viereck ein Quadrat sein soll. Sorry
Die Punkte lauten Q (7/5/0) und S (3/2/0).
dann sind ja jetzt alle notwendigen Informationen da ;-)
Mit Vektoren komme ich besser zurecht.
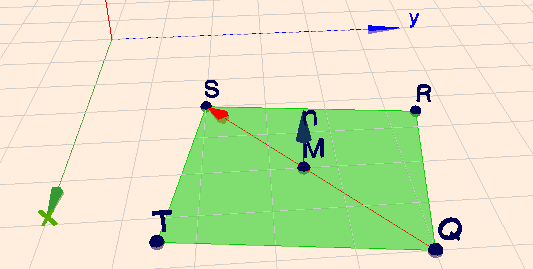
dann mache ich es vektoriell: Man berechne zunächst den Mittelpunkt \(M\) des Quadrats $$M = \frac 12 (Q + S) =\frac 12 \left( \begin{pmatrix} 7\\ 5\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} + \begin{pmatrix} 3\\ 2\\ 0 \end{pmatrix}\right) = \begin{pmatrix} 5\\ 3,5\\ 0 \end{pmatrix}$$dann den Vektor \(e\) der Diagonalen$$e = \vec{QS} = S - Q = \begin{pmatrix} 3\\ 2\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} - \begin{pmatrix} 7\\ 5\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} -4\\ -3\\ 0 \end{pmatrix}$$Mit der Vorgabe, dass sich das Quadrat in der xy-Ebene befindet, ist auch der Normalvektor \(n\) dieser Ebene gegeben. Dann bekommt man den Vektor \(f = \vec{RT}\) der Gegendiagonalen aus dem Kreuzprodukt \(n \times e\). \(n\) muss dazu die Länge \(1\) haben.$$f = n \times e = \begin{pmatrix} 0\\ 0\\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \times \begin{pmatrix} -4\\ -3\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 3\\ -4\\ 0 \end{pmatrix}$$und die fehlenden Punkte \(R\) und \(T\) berechnen sich nun nach $$\begin{aligned} R &= M - \frac 12 f = \begin{pmatrix} 3,5\\ 5,5\\ 0 \end{pmatrix} \\ T &= M + \frac 12 f = \begin{pmatrix} 6,5\\ 1,5\\ 1 \end{pmatrix} \end{aligned}$$Das ganze nochmal zur Veranschaung in Geoknecht3D (klick auf das Bild)
Gruß Werner