Aufgabe:
Text erkannt:
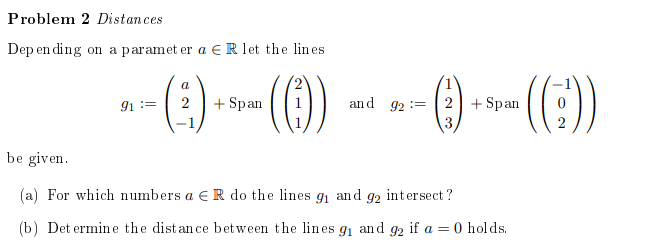
Problem 2 Distances
Depending on a paramet er \( a \in \mathbb{R} \) let the lines
\( g_{1}:=\left(\begin{array}{c} a \\ 2 \\ -1 \end{array}\right)+\operatorname{Span}\left(\left(\begin{array}{l} 2 \\ 1 \\ 1 \end{array}\right)\right) \quad \text { and } g_{2}:=\left(\begin{array}{l} 1 \\ 2 \\ 3 \end{array}\right)+\operatorname{Span}\left(\left(\begin{array}{c} -1 \\ 0 \\ 2 \end{array}\right)\right) \)
be given.
(a) For which numbers \( a \in \mathbb{R} \) do the lines \( g_{1} \) and \( g_{2} \) intersect?
(b) Determine the distance between the lines \( g_{1} \) and \( g_{2} \) if \( a=0 \) holds.
Ist für b) d = 9/4 richtig?
Text erkannt:
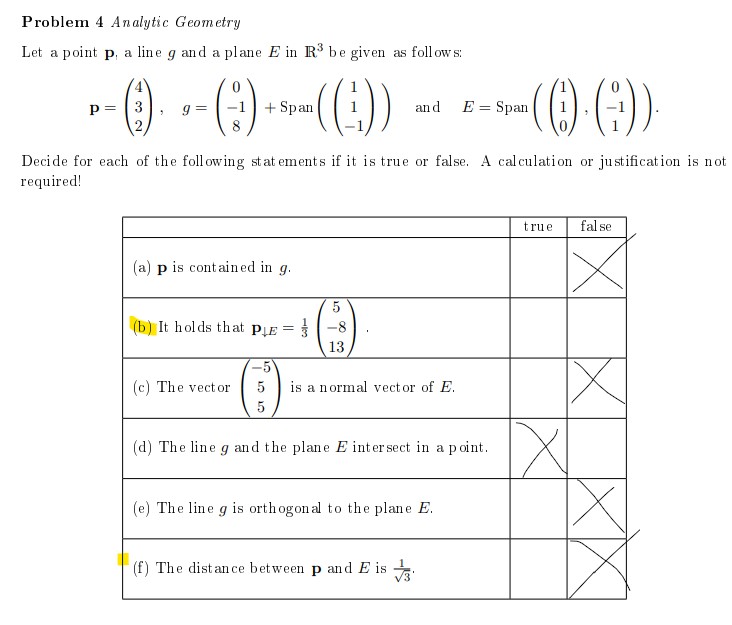
Problem 4 Analytic Geometry
Let a point \( \mathbf{p} \), a line \( g \) and a plane \( E \) in \( \mathbb{R}^{3} \) be given as follows:
\( \mathbf{p}=\left(\begin{array}{l} 4 \\ 3 \\ 2 \end{array}\right), \quad g=\left(\begin{array}{c} 0 \\ -1 \\ 8 \end{array}\right)+\operatorname{Span}\left(\left(\begin{array}{c} 1 \\ 1 \\ -1 \end{array}\right)\right) \quad \text { and } \quad E=\operatorname{Span}\left(\left(\begin{array}{l} 1 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end{array}\right),\left(\begin{array}{c} 0 \\ -1 \\ 1 \end{array}\right)\right) . \)
Decide for each of the following statements if it is true or false. A calculation or justification is not required!
\begin{tabular}{|l|l|l|}
\hline & true & false \\
\hline (a) \( \mathbf{p} \) is contained in \( g \). & \\
\hline (b) It holds that \( \mathbf{p}_{\downarrow E}=\frac{1}{3}\left(\begin{array}{c}5 \\ -8 \\ 13\end{array}\right) \). & \\
\hline (c) The vector \( \left(\begin{array}{c}-5 \\ 5 \\ 5\end{array}\right) \) is a normal vector of \( E \). & \\
\hline (d) The line \( g \) and the plane \( E \) intersect in a point. & \\
\hline (e) The line \( g \) is orthogonal to the plane \( E \). & \\
\hline (f) The distance between \( \mathbf{p} \) and \( E \) is \( \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \). & \\
\hline
\end{tabular}
Ich weiß nicht weiter bei b).