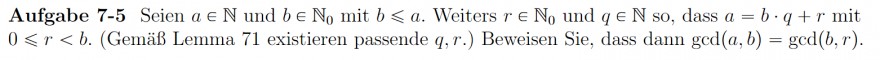
Text erkannt:
Aufgabe \( 7-5 \) Seien \( a \in \mathbb{N} \) und \( b \in \mathbb{N}_{0} \) mit \( b \leqslant a \). Weiters \( r \in \mathbb{N}_{0} \) und \( q \in \mathbb{N} \) so, dass \( a=b \cdot q+r \) mit \( 0 \leqslant r<b \). (Gemäß Lemma 71 existieren passende \( q, r \).) Beweisen Sie, dass dann \( \operatorname{gcd}(a, b)=\operatorname{gcd}(b, r) \).

Text erkannt:
Lemma 71 Let \( a \in \mathbb{N} \) and \( b \in \mathbb{Z} \). Then there exist a unique quotient \( q \in \mathbb{Z} \) and a unique remainder \( r \in \mathbb{N}_{0} \) such that
$$ b=a \cdot q+r \quad \text { and } \quad 0 \leq r<a . $$
Text erkannt:
Lemma 71
Let \( a \in \mathbb{N} \) and \( b \in \mathbb{Z} \). Then there exist a unique quotient \( q \in \mathbb{Z} \) and a unique remainder \( r \in \mathbb{N}_{0} \) such that
$$ b=a \cdot q+r \quad \text { and } \quad 0 \leq r<a . $$
We will use the operators div and mod for computing the divisor and remainder. That is, \( q \) and \( r \) of Lemma 71 are given by \( q:=b \) div \( a \) and \( r:=b \bmod a \).
\( = \) The modulo of powers of 2 can be expressed as a bitwise AND operation:
$$ b \bmod 2^{n}==b \&\left(2^{n}-1\right) $$
In many programming languages the remainder \( r \) can be obtained by means of the modulo operator. See, e.g., the operator \% in C, C++, C#, Java, and Perl.