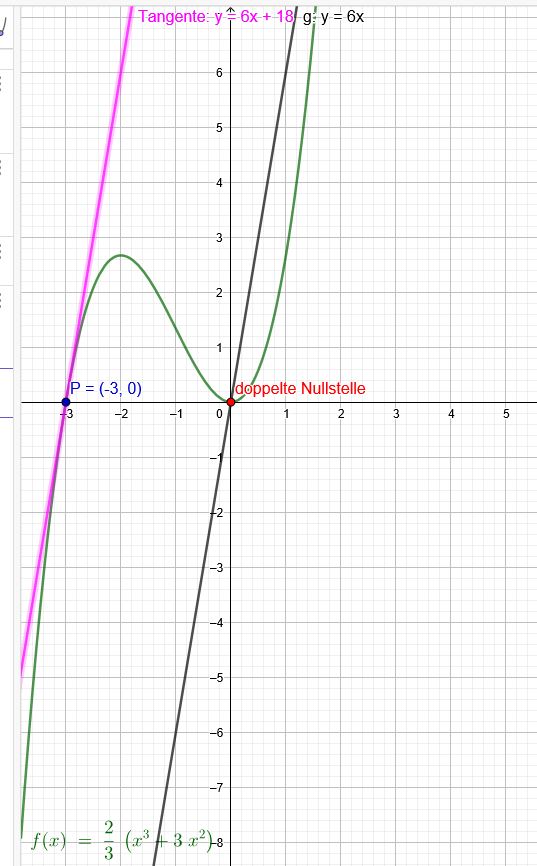
Bestimmen Sie die ganzrationale Funktion dritten Grades, deren Graph
a) die \( \mathrm{x} \)-Achse im Ursprung berührt und deren Tangente in \( \mathrm{P}(-3 | 0) \) parallel zur Geraden \( \mathrm{y}=6 \mathrm{x} \) ist.
Doppelte Nullstelle Ursprung und einfache Nullstelle \( \mathrm{P}(-3 | 0) \):
\(f(x)=a \cdot x^2 \cdot(x+3)=a\cdot (x^3+3x^2)\)
Tangente in \( \mathrm{P}(-3 | 0) \) hat die Steigung \(m=6 \)
\(f'(x)=a\cdot [3x^2+6x]\)
\(f'(-3)=a\cdot [3\cdot (-3)^2+6\cdot (-3)]=9a\)
\(9a=6\)
\(a=\frac{2}{3}\)
\(f(x)=\frac{2}{3}\cdot (x^3+3x^2)\)