f(x) = xx = (eln(x))x = ex·ln(x)
Kettenregel und für die innere Ableitung Produktregel:
f '(x) = ex·ln(x) · (ln(x) + 1) = ex·ln(x) · [ ln(x) + 1) ] ' = ex·ln(x) * ( 1 * ln(x + x * 1/x )
Nach Kommentar von jc2144 korrigiert:
= ex·ln(x) * ( ln(x) +1) = 0 ⇔ x = e-1 mit VZW von - → +
→ f ist nicht streng monoton steigend.
b) → T( e-1 | e^{- e^{-1}} ≈ ( 0.3678794411 | 0.6922006275 ) ist lokales Minimum
Wegen \(\lim_{x \to 0} f(x) \) = 1 > f( e-1) und \(\lim_{x \to i∞} f(x) \) = ∞
ist das auch ein globales Minimum
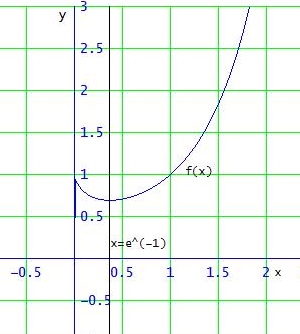
ist das auch ein globales Minimum
c) globale und lokale Maxima gibt es nicht.
Gruß Wolfgang