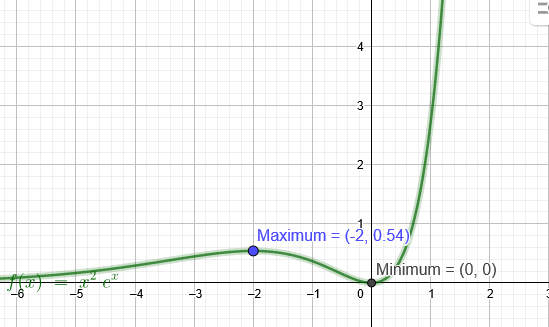
\( f(x)=x^{2} \cdot e^{x} \)
f´(x)=2x*\( e^{x} \)+\( x^{2} \) *\( e^{x} \)=\( e^{x} \)*(\( x^{2} \) +2x)
\( e^{x} \)*(\( x^{2} \) +2x)=0 \( e^{x} \) kann nicht 0 werden.
\( x^{2} \) +2x=0
x*(x+2)=0
x₁=0 \( f(0)=0^{2} \cdot e^{0} \)=0
x₂=-2 \( f(-2)=(-2)^{2} \cdot e^{-2} \)=\( \frac{4}{e^2} \)
Art der Extremwerte:
f´´(x)=\( e^{x} \)*(\( x^{2} \) +2x)+\( e^{x} \)*(2x+2)
f´´(0)=\( e^{0} \)*(\( 0^{2} \) +2*0)+\( e^{0} \)*(2*0+2)=2>0 Minimum
f´´(-2)=\( e^{-2} \)*(\( (-2)^{2} \) +2*(-2))+\( e^{-2} \)*(2*(-2)+2)=-\( \frac{2}{e^2} \)<0 Maximum