
Text erkannt:
globales Extrema:
\( \begin{array}{l} f(x)=x^{2} e^{-x^{2}} \\ x=0,-1,1 e[-2,2] \\ f(0)=0 \\ f(-1)=(-1)^{2} \cdot e^{-(-1)^{2}}=1 \cdot e^{1}=e \\ f(1)=(1)^{-(4)^{2}}=e \\ f(-2)=(-2)^{2} \cdot e^{-(-2)^{2}}=4 \cdot e^{-4} \\ f(2)=2^{2} \cdot e^{-(2)^{2}}=4 \cdot e^{4} \end{array} \)
globales Minimm Liegt bei \( x=0 \) und gldbales Maxmum liegt bei \( x=1 \) and \( x=-1 \)
Aufgabe:
Hier kommt die Aufgabe 3:

Text erkannt:
Aufgabe 3. (10 Punkte) Bestimmen Sie alle lokalen und globalen Extrema der Funktion
\( f:[-2,2] \rightarrow \mathbb{R}, \quad f(x)=x^{2} e^{-x^{2}} \)
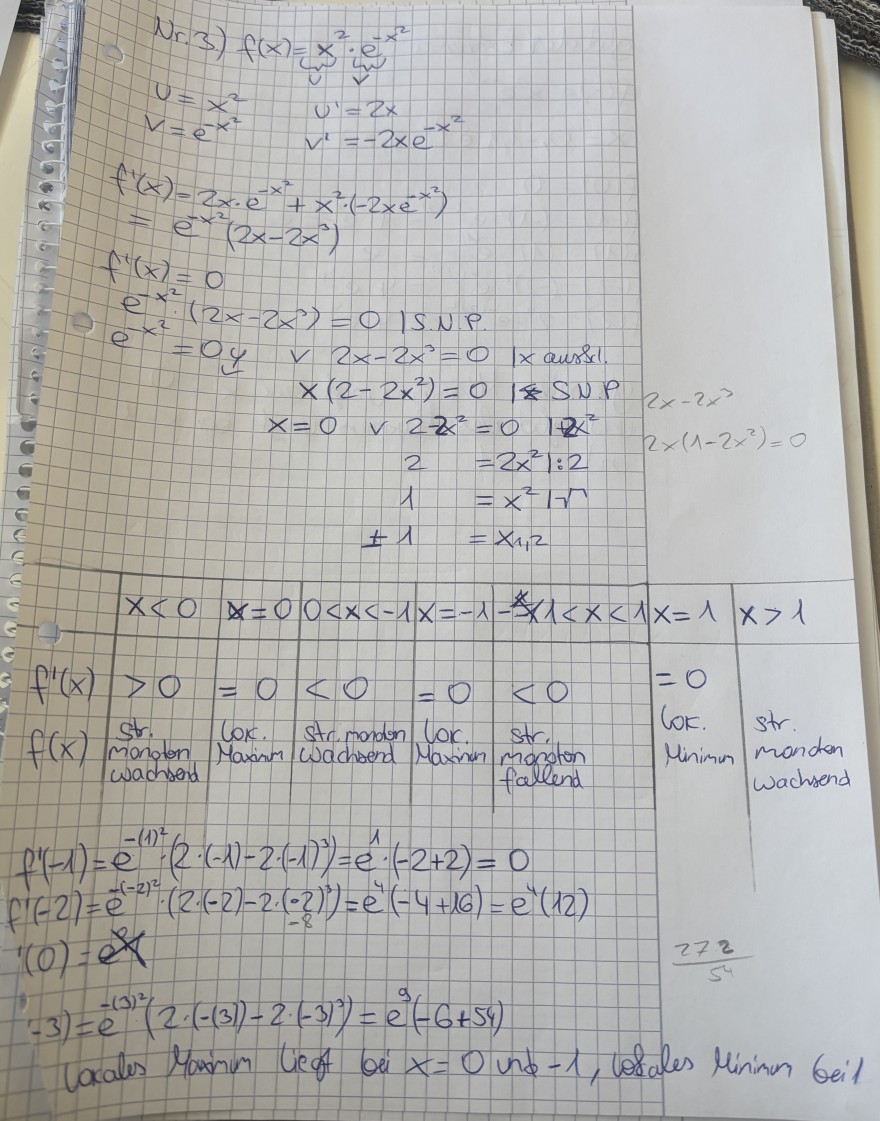
Text erkannt:
Nr.3) \( f(x)=\underbrace{x}_{y} \cdot \sum \limits_{y} e^{-x^{2}} \)
7
\( \frac{1}{5} \)
\( \vdots \)
\( \vdots \)
\( \begin{array}{ll} v=x^{2} & v^{\prime}=2 x \\ v=e^{-x^{2}} & v^{\prime}=-2 x e^{-x^{2}} \end{array} \)
\( \begin{array}{l} f^{\prime}(x)=2 x \cdot e^{-x^{2}}+x^{2} \cdot\left(-2 x e^{-x^{2}}\right) \\ =e^{-x^{2}}\left(2 x-2 x^{3}\right) \\ f^{\prime}(x)=0 \\ e^{-x^{-}} \cdot\left(2 x-2 x^{3}\right)=0 \text { IS.N. } . \\ =04 \vee 2 x-2 x^{3}=0 \quad 1 x \text { aussi. } \\ x\left(2-2 x^{2}\right)=0 \text { SNP } \\ x=0 \vee 2-2 x^{2}=0 \quad 1-2 x^{2} \\ 2=2 x^{2} \mid: 2 \\ 1=x^{2} \mid \top \\ \pm 1=x_{1,2} \end{array} \)
\( \begin{array}{l} f^{\prime}(-1)=e^{-(1)^{2}} \cdot\left(2 \cdot(-1)-2 \cdot(-1)^{3}\right)=e^{1} \cdot(-2+2)=0 \\ f^{\prime}(-2)=e^{-(-2)^{2}} \cdot\left(2 \cdot(-2)-2 \cdot(-2)^{3}\right)=e^{4}(-4+16)=e^{4}(12) \\ (0)=e^{4} \\ (-3)=e^{-(3)^{2}}\left(2 \cdot(-(3))-2 \cdot(-3)^{3}\right)=e^{9}(-6+54) \end{array} \)
272
Lacales Manmm Lieot bei \( x=0 \) und -1 , Losales Miniman beil
